Ground Collision Avoidance in an RTA architecture
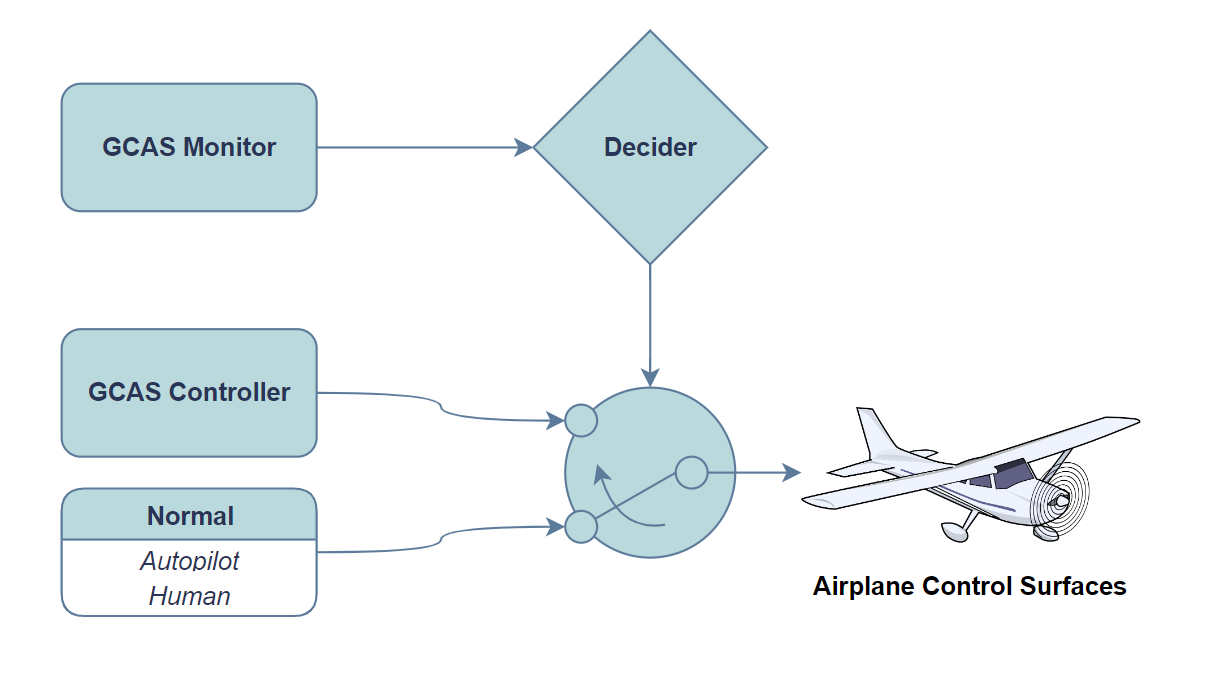
This section highlights the high-level architecture for the Real-Time Assurance (RTA) for openGCAS. The high level RTA figure contains a generic diagram for any RTA control system. The RTA is responsible for selecting between a number of different control systems in real time. For example, the diagram contains one primary control system called the Complex Function. The Complex Function is either human control or autopilot. Running in parallel to the Complex Function are the Recovery Control Functions. Their sole purpose is to provide an escape route in a potentially fatal scenario. In addition, a monitor is required to select between the different control systems in an imminent fatal event. The selector is known as the Safety Monitor.
Now, the generic diagram described in the previous section will be translated into a specific implementation for openGCAS. At any given moment, both the GCAS Monitor and the GCAS Controller are evaluating the scenario at present, planning an escape to a fatal event should one arise. The GCAS Monitor's role is a high level evaluation of the situation as a whole, performing calculations to Determine Need to Avoid (DNA.) The GCAS Monitor's evaluation of the situation is sent to the "Decider", where a switch can be toggled between normal (human or autopilot) control and GCAS control.